🧬 NAD+ in 2025: What the Latest Science Really Says
The Molecule Biohackers Love — But Does the Science Still Support It?
What is NAD+?
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) is a coenzyme found in every cell. It's essential for:
🧬 DNA repair
⚡ Mitochondrial energy production
🧠 Brain cell communication
🔄 Metabolic function and circadian rhythm
🛡️ Immune response and cellular defense
NAD+ works as a molecular switchboard operator — transferring electrons, turning enzymes on and off, and fueling sirtuins (key longevity regulators). It's no surprise biohackers have latched onto it.
NAD+ declines with age — sometimes by up to 50% by middle age. That decline is associated with fatigue, poor recovery, inflammation, and signs of accelerated aging.
So, the theory is simple:
👉 Replenish NAD+ = Restore youth.
But does it work like that in real life?
Why Biohackers Are Taking It
From $15 capsules to $1,500 infusions, NAD+ has become the centerpiece in:
Longevity protocols
Energy and focus stacks
Cognitive support and neuroprotection
Post-COVID and burnout recovery clinics
Anti-aging dermatology treatments
Most NAD+ boosters use precursors like nicotinamide riboside (NR) or nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) — easier to absorb and convert inside the body.
Some go further with intravenous NAD+ infusions for "immediate mitochondrial activation" and anti-aging benefits.
But does the research support all of this?
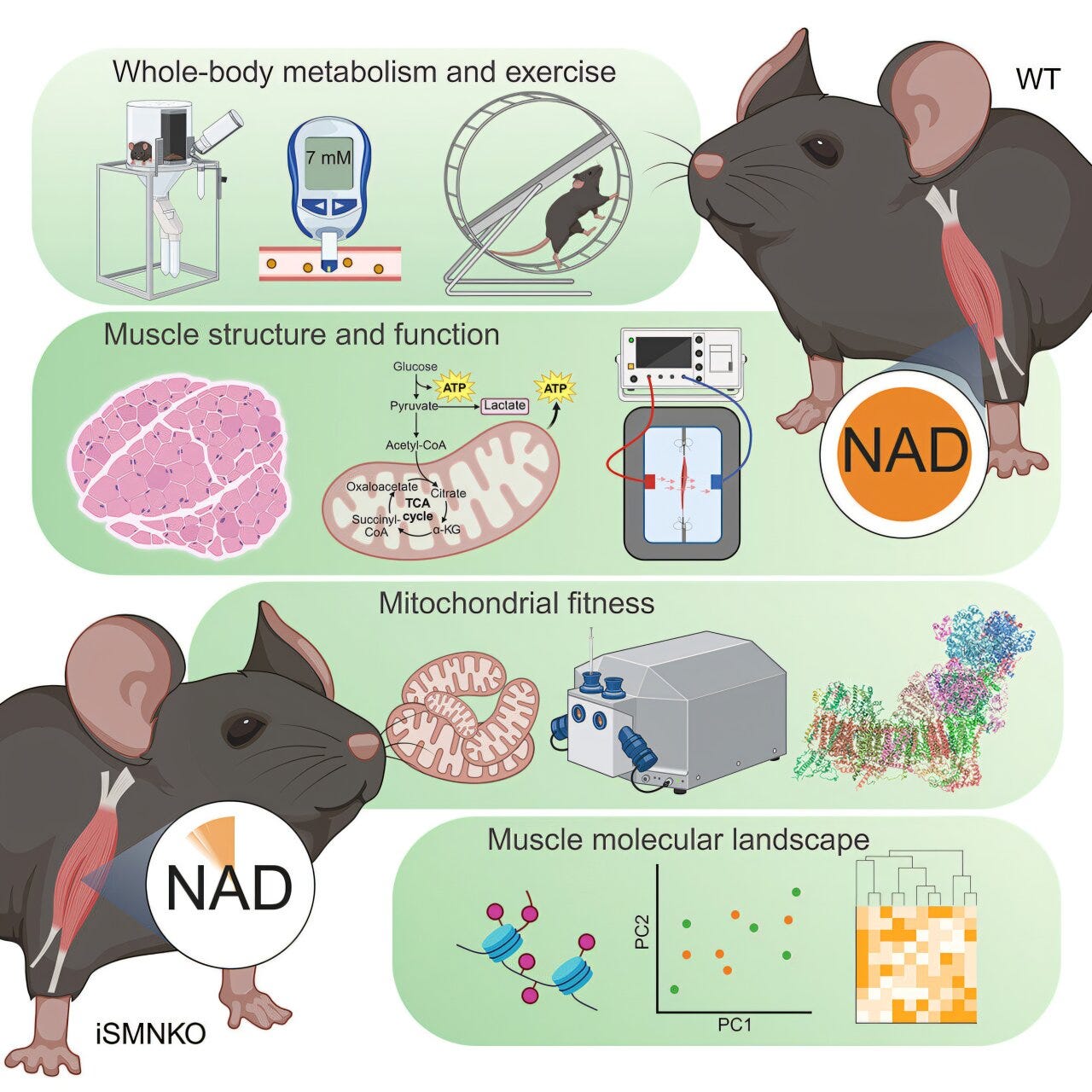
📉 BREAKING: Muscle NAD+ Can Drop by 85% — and Still Function
A bombshell study published in Cell Metabolism (2025) looked at adult mice whose skeletal muscle NAD+ levels were depleted by 85%.
👉 The result? No loss in strength. No metabolic decline. No signs of early aging.
Even DNA repair and epigenetic markers remained stable.
🧠 Implication: If muscles — our most energy-demanding tissue — don’t falter with very low NAD+, maybe we’ve overestimated its role in functional aging.
💉 NAD+ IVs — Popular, Expensive… and Largely Ineffective?
NAD+ infusions are trending in elite wellness circles. But molecular biology studies tells a different story.
The NAD+ molecule is large and charged — meaning it cannot easily cross cell membranes. So, while it circulates in the bloodstream, it may not enter the cells where it's needed.
Worse, high doses can cause:
Nausea
Headaches
Heart palpitations
Digestive discomfort
🧠 Implication: You might feel something after a drip — but it’s likely due to hydration, placebo, or stress recovery… not mitochondrial magic.
💊 NAD+ Precursors: NR & NMN — Do They Work?
In contrast to IV NAD+, oral supplements focus on giving your body what it needs to build its own NAD+.
One study using a combined NR/NMN supplement showed a 26.5% increase in whole blood NAD+ after four weeks.
But results varied widely. And improvements in energy, mood, or cognition? Inconsistent and mostly subjective.
🧠 Implication: Supplements can raise levels — but real benefits? Still murky. Not a miracle.
🔬 So What Actually Supports NAD+?
Lifestyle — not lab-made molecules — remains the most reliable NAD+ strategy.
⛅ Fasting and caloric restriction
🔥 Sauna or hyperthermia exposure
❄️ Cold exposure (e.g., ice baths)
🏃 HIIT or sprint training
🛌 Circadian-aligned sleep
These interventions upregulate the NAD+ salvage pathway and activate sirtuins — with no side effects or $1,000 drips.
My Thoughts
Yes, NAD+ is crucial.
Yes, it declines with age.
But boosting NAD+ isn’t a guaranteed shortcut to vitality.
We need to be cautious. Not anti-supplement — just evidence-driven.
For now: prioritize lifestyle, track your own biomarkers, and be wary of silver bullets.